

International Training Outline:
Administration | Application Settings
Maintenance | Document Manager
Maintenance | Export Licenses (OPT)
Epicor | Material Management | Inventory Management | Setup | Part_Maintenance
Process a NAFTA shipment from Epicor
Process a NON-NAFTA shipment from Epicor
Administration | Application Settings
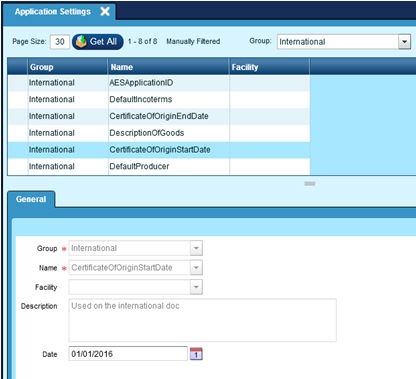
8 International Entries:
|
International |
AESApplicationID |
Drop Down Options: |
|
International |
AESEMailAddresses |
Enter comma separated list of email addresses that will receive ITN email notifications from AES upon completing a successful filing. If no application setting then the email address sent in the filing request will use the login user email address. |
|
International |
CertificateOfOriginEndDate |
Used on International Documents. |
|
International |
CertificateOfOrigStartDate |
Used on International Documents. |
|
International |
DefaultIncoTerms |
Sets the default Inco terms for International Documents. |
|
International |
DefaultProducer |
Sets the default Producer for International Documents. |
|
International |
DefaultReasonForExport |
Sets the default Reason for Export for International Documents. |
|
International |
DescriptionOfGoods |
Sets the default Description of Goods for International Documents. |
SCAC:
Enter the Standard Alpha Character Code used to identify this carrier. This code will print on the International Paperwork forms.
SCAC Code Examples:
YFSY – Yellow Freight
RDWY – Roadway Express
ABFS - ABF Freight System Inc
FDEG - FedEx FDCC - FedEx Custom Critical
FEXF - FedEx Freight
Maintenance | Document Manager
The Document Manager screen, located in the Maintenance menu, is the report hub for the bill of lading, international paperwork and non-carrier specific manifest reports. This screen is the foundation for company documents. It is used to define the various documents in the system as defaults, set where they are located, and define their default printer behavior.
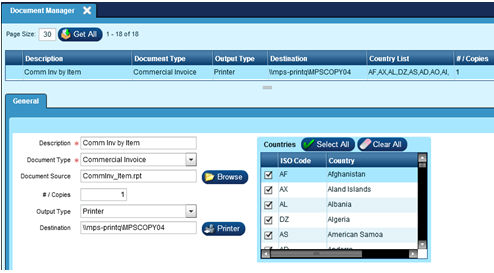
NOTE: Recommend updating/adding to this file from the Server.
The hierarchy of four screens involved with setting up reports and printing:
Document Manager
Carriers | Documents
Workstations | Documents
Customers | Documents.
During the installation of Print Monitor, Crystal Reports run time was also installed with report templates for International Paperwork, Generic Carrier Label, Bill of Lading, Manifest Reports and HazMat paperwork. These report templates are typically located in folder C:\InsiteReports on the server where the Print Monitor is installed.
The folder where the Print Monitor looks for print jobs was also created and is typically located at C:\InsitePrintFiles. This is where you can see the files that were created for printing and use the log file to trouble shoot printing issues. If the .mon file changes to .bad; there is an issue with the print job. If it was sent to the printer successfully then the .mon file will be deleted or moved to the archive folder depending on the user’s print mon settings.
The Tariff Codes module records the Schedule B tariff code classifications which encompass all the products to be exported by the shipper. These records are used for creating export documentation and for electronic filing of the shipper's export declaration. Each Product record should be assigned to a Tariff Code classification to ensure that export documentation is completed accurately in order for duties and taxes to be calculated correctly based on the origin/destination countries of the shipment.
General Tab:
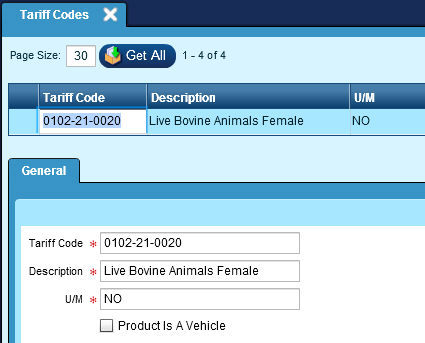
Tariff Code:
Enter the 10-digit tariff code. You can go to
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/reference/codes/index.html for a current listing of Schedule B numbers.
U/M:
Enter the Export UOM. NOTE this may not be the stock UOM.
It is important that the shipper ship quantities in the unit of measure that is defined for the specific Schedule B Class that the commodity falls in to, and that the item’s unit weight is entered in pounds. For example, any commodity that falls under Schedule B Class 7318.21.0000 (Spring washers and other lock washers) must be reported in kilograms. Failure to ship in quantities of kilograms could cause a filing to be incorrect because ISS will upload the packed quantity and AES will assume this to be in kilograms. This could create a filing to be incorrect if the shipper packed using number of units vs. total kilograms.
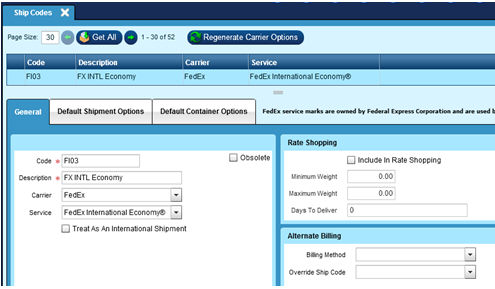
Service:
Map Ship Code to appropriate International Service.
NOTE:
All FedEx ShipCodes MUST have a Duty/Tax Payor option checked.
UPS Assumes Recipient unless you send a different option.
This module is used to define and manage the countries of the world and the various characteristics of them. Epicor Manifest Software provides a country list with this information to import with the data packager. Be sure to add the districts required for each country as well.
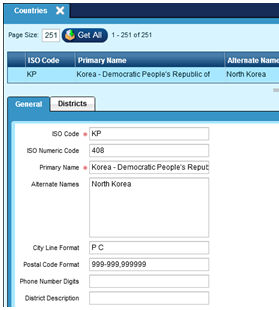
General Tab:
Alternate Names:
Defines any alternate names for the country. Alternate names in this list must be separated by commas and can be used to link this countries list to the ERP data.
NOTE: The Country Name in Epicor must exactly match the Insite Country Primary Name OR one of the Alternate Names.
i.e. If Epicor has Republic of South Korea…there is NO Republic of South Korea entry.
It must be ‘Korea – Republic of’ or just ‘South Korea’.
Maintenance | Export Licenses (OPT)
The Export Licenses module is used to show the licenses that are available and can be selected and associated with a given shipment. An Export License is a specific grant of authority from the government to a particular exporter to export a specific product. Licenses are granted on a case by case basis for either a single transaction or for a specified period of time. The exporter must apply for the export license. License can be at the commodity level in addition to a specific country or specific customer. License information, in general, is able to be overridden at the shipment level.
Licenses are a shipment construct and are determined by the product being shipped and destination. You can use Maintenance/Export Licenses to create the licenses that you have been approved for and then they are available to assign in Intl paperwork.
The Maintenance/Export License record can be created using different filters so you can create for a specific product/destination country/ date range combinations and the Intl paperwork will display only licenses in the lookup that match the shipment – or you can enter on-the-fly.
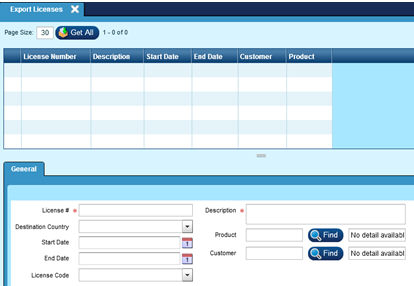
License #:
This required field is used to define the License number for the currently selected Export License
Destination Country:
This drop down is used to select the country to export to. This drop down is populated by the countries in the Country table.
Start Date:
This field is used to define the starting date that the currently selected export license is valid
End Date:
This field is used to define the ending date that the currently selected export license is valid
License Code:
This drop down is used to select the applicable license code for the currently selected export license. The options in this drop down are populated via Misc Codes.
Description:
This required field is used to define the extended description for the currently selected export license
Product:
This field is used to associate a product with the currently selected export license
Customer:
This field is used to associate a customer with the currently selected export license.
Epicor | Material Management | Inventory Management | Setup | Part Maintenance
Required International Fields that will pull into MANIFEST if populated:
Detail SubTab:
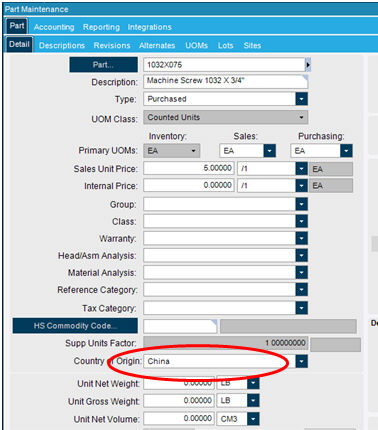
Country Of Origin:
Select Country of Origin from the pull down.
If Country is NOT in list, right click on the Part Country of Origin field (Not the Label).
Select Open With…..Country Entry
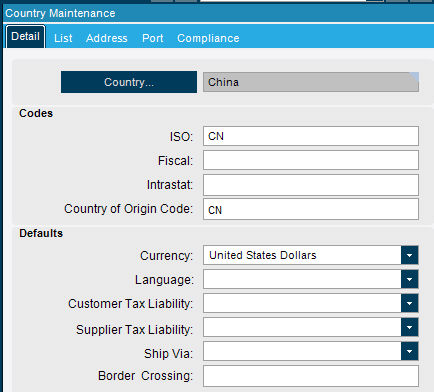
Create new country code OR enter the correct ISO Country code. (See Country Listing in Manifest.)
Integrations Tab:
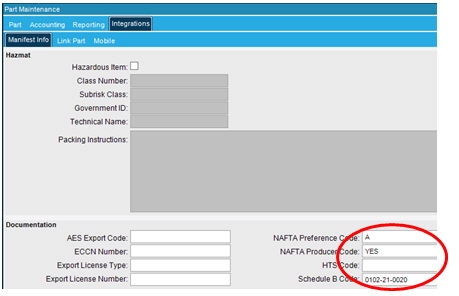
NAFTA Preference Code:
Enter appropriate NAFTA Preference Code. NAFTA Preference Code must be a single letter.(A, B, C, D, E, or F) See below for further description.
The NAFTA preference criteria designated by the letters “A” through “F” show how your product qualifies for a NAFTA tariff rate. A preference criterion is required in Field #7 of the Certificate of Origin for each export product.
NAFTA Producer Code:
Schedule B Code:
Enter the 10 digit code with dashes for the part.
Field Definition Information:
AES Export Codes:
CH-GOODS DONATED FOR RELIEF OR CHARITY
CI-IMPELLED SHIPMENTS OF GOODS DONATED FOR RELIEF OR CHARITY
CR-GOODS MOVING UNDER A CARNET
DD-OTHER EXEMPTIONS
FI-IMPELLED FOREIGN MILITARY SALES
FS-FOREIGN MILITARY SALES
GP-U.S. GOVT. CONTRACT FOR OVERSEAS CONTRUCTION
GS-EXPORTS FOR EXCLUSIVE USE OF U.S. GOVT AGENCIES
HH-PERSONAL AND HOUSEHOLD EFFECTS AND TOOLS OF TRADE
HV-PERSONALLY OWNED VEHICLES
IP-IMPORTED TEMPORARILY FREE UNDER BOND EXPORTED AFTER PROCESSING IN U.S.
IR-IMPORTED TEMPORARILY FREE UNDER BOND EXPORTED AFTER REPAIR OR ALTERATION IN U.S.
IS-IMPORTED TEMPORARILY FREE UNDER BOND EXPORTED IN SAME CONDITION
IW-SHIPMENTS DESTINED TO INTERNATIONAL WATERS
MS-EXPORTS FOR EXCLUSIVE USE OF U.S. ARMED FORCES
OI-OTHER IMPELLED EXPORTS
OS-GENERAL EXPORTS (ALL OTHERS)
TE-TEMPORARY EXPORT OF GOODS FOR RETURN TO U.S. IN SAME COND.
TL-MERCHANDISE EXPORTED ON LESS THAN 1 YEAR LEASE
TP-TEMPORARY EXPORT OF DOMESTIC GOODS FOR PROCESSING AND RETURN
UG-SINGLE GIFT PARCELS
ZD-N A F T A DUTY DEFERRAL SHIPMENTS
ECCN:
ECCN, stands for Export Control Classification Number. An ECCN is an alpha-numeric classification used in the Commerce Control List to identify items for export control purposes. An ECCN is different from a Schedule B number, which is used by the Bureau of Census to collect trade statistics. It is also different from the Harmonized Tariff System Nomenclature, which is used to determine import duties.
All ECCNs will have 5 characters, for example, 1A001, 4B994, or 8D001. There are 10 categories on the Commerce Control List. The first number of the ECCN identifies the category to which it belongs, for example, 1 = Nuclear Materials Facilities and Equipment, 4 = Computers, 9 = Propulsion Systems, Space Vehicles and Related Equipment.
However, EAR99 is a different type of classification. It serves as a "basket" designation for items that are covered by the EAR, but are not specified on the Commerce Control List. EAR99 items can be shipped without a license to most destinations under most circumstances. There are limitations on the use of EAR99. However, the majority of the commercial exports from the United States fall into this category.
A key in determining whether an export license is needed from the Department of Commerce is finding out if the item you intend to export has a specific Export Control Classification Number (ECCN). ECCNs are five character alpha-numeric designations used on the Commerce Control List (CCL) to identify dual-use items for export control purposes. An ECCN categorizes items based on the nature of the product, i.e. type of commodity, software, or technology and its respective technical parameters.
An ECCN is different from a Schedule B number, which is used by the Bureau of Census to collect trade statistics. It is also different from the Harmonized Tariff System Nomenclature, which is used to determine import duties.
All ECCNs are listed in the Commerce Control List (CCL) (Supplement No. 1 to Part 774 of the EAR), which is divided into ten broad categories, and each category is further subdivided into five product groups. The first character of the ECCN identifies the broader category to which it belongs and the second character identifies the product group (see example and boxes below).
If Your Item is Not on the Commerce Control List - EAR99
If your item falls under the jurisdiction of the U.S. Department of Commerce and is not listed on the CCL, it is designated as EAR99. The majority of commercial products are designated EAR99 and generally will not require a license to be exported or reexported. However, if you plan to export an EAR99 item to an embargoed or sanctioned country, to a party of concern, or in support of a prohibited end-use, you may be required to obtain a license.
NAFTA Preference Code:
Preference Criterion A
Preference Criterion A corresponds to goods wholly obtained or produced entirely in Canada, Mexico or the United states.
For a good to qualify under this criterion, it must contain NO non-North American parts of materials anywhere in the production process. It is generally reserved for basic products such as those harvested, mined, or fished in the NFTA territory, although it would include a manufactured good with NO non-NAFTA inputs.
As a general rule, however, Preference Criterion A rarely applies to manufactured goods. If the god contains ANY non-FAFTA materials, it will not qualify under Preference Criterion A.
Preference Criterion B
Even if you good contains non-NAFTA materials, it can qualify a B if the materials satisfy the Rules of Origin. The Annex 401 Rules of Origin are based on a change in tariff classification, a regional value-content requirement, or both.
The updated Rules of Origin are located in General Note 12(t) of the NAFTA. Preference Criterion B is used when the good being certified is produced using materials that the producer/exporter is unable to prove qualify as originating goods in their own right. The finished product will be originating if the requirements of the applicable rule of origin are met. The requirements of the NAFTA Rules of Origin differ from good to good.
Preference Criterion C
This criterion corresponds to goods produced entirely in Canada, Mexico, and/or the United States exclusively from NAFTA materials.
Preference Criterion C is used when the producer/exporter is able to document that the finished good is produced entirely in the NAFTA territory using only materials that would qualify in their own right. The producer/exporter should have documented proof that every raw material and component is a NAFTA good.
Preference Criterion D
Goods are produced in the territory of one or more of the NAFTA countries but do not meet the applicable rule of origin, set out in Annex 401, because certain non-originating material do not undergo the required change in tariff classification. The good do none the less meet the regional value-content requirement specified in Article 401(d). This criterion is limited to the following two circumstances:
1 – The good was imported into the territory of a NAFTA country in an unassembled or disassembled form but was classified as an assembled good, pursuant to H>S> General Rule of Interpretation 2(a), or
2 – The good incorporated one of more non-originating materials, provided for as parts under the H.S., which could not undergo a change in tariff classification because the heading provided for both the good and its parts and was not further subdivided into subheadings, or the subheading provided for both the good and its parts and was not further subdivided.
Preference Criterion E
This criterion applies to certain automatic data processing goods and their parts, specified in Annex 308.1.
Preference Criterion F
Preference Criterion F applies to certain agricultural goods imported into Mexico. For more information, please call the U.S. Foreign Agricultural Service at (202) 720 – 7420.
The good is an originating agricultural good under preference criterion A,B, or C above and is not subject to a quantitative restriction in the importing NAFTA country because it is a “qualifying good” as defined in Annex 703.2, Section A or B(please specify). A good listed in Appendix 703.2B.7 is also exempt from quantitative restrictions and is eligible for NAFTA preferential tariff treatment if it meets the definition of “qualifying good” in Section A of Annex 703.2.
NOTE 1: This criterion does not apply to goods that wholly originated in Canada or the United States and are imported into either country.
NOTE 2: A tariff rate quota is not a quantitative restriction.
NAFTA Producer Code:
Enter one of the following: Yes, NO(1), NO(2), NO(3) based on the following definitions:
YES = you are the producer of the good.
NO(1) = you are not the producer of the good, but are able to fill out the Certificate based upon your knowledge of whether the good qualifies.
NO(2) = you are not the producer but are relying upon written representation from the producer (other than the Certificate of Origin) that the good qualifies.
NO(3) = you are not the producer but have a NAFTA Certificate of Origin for the good provided to you voluntarily by the producer.
Process a NAFTA shipment from Epicor
After 'Freighting' a NAFTA Shipment, Go to Manifest | Shipping Screen and Find shipment.
Select Forms | International PaperWork | Documents Tab:
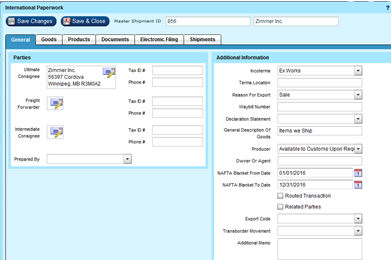
Select forms you wish to print and click on the Print icon.
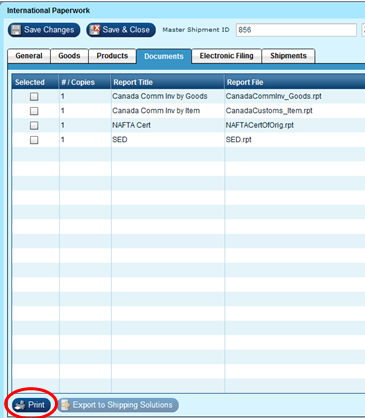
Process a NON-NAFTA shipment from Epicor
After 'Freighting' a NAFTA Shipment, Go to Manifest | Shipping Screen and Find shipment.
Select Forms | International PaperWork | Documents Tab and print appropriate forms,
Information on Exemptions:
The exemption legend from 15 CFR Part 30 indicates why the shipment is not required to be filed through AES. Some examples:
Shipments to Canada: NOEEI 30.36
Schedule B value < $2500.00 and no license required: NOEEI 30.37(a)
Miscellaneous exemptions: NOEEI 30.37(b thru u) where b thru u = the appropriate statement from 15 CFR 30.37
UPS International Paperless Settings:
There is no additional setup required for using UPS Paperless. If your contract with UPS has a Paperless clause, all International shipments will be considered Paperless. UPS Paperless forms include Commercial Invoice, Certificate of Origin and NAFTA certificate.
FedEx Electronic Trade Documents:
See Help files for Procedures | FedEx ETD Electronic Trade Documents
LTL - Shipments by Truck:
Shipping documents used to transport the shipment (BOL, Air Waybill, etc.) must be annotated to include the proof of filing citation (i.e. ITN number) which is assigned by AES and identifies that the export information has been accepted by AES.
In the Special Instruction field in the BOL screen, paste the ITN number.